Subtotal $0.00
Introduction
In recent years, advancements in sensor technology have propelled innovations in 3D imaging and augmented reality (AR), opening up exciting new possibilities across various industries. Among these advancements, Time-of-Flight (ToF) sensors have become one of the most significant developments, playing a crucial role in shaping the capabilities of 3D imaging and AR. ToF sensors are known for their high precision, ability to capture depth information and integration into various devices. Their application in augmented reality and 3D imaging has revolutionized how we interact with digital content and the physical world.
Definition
A Time-of-Flight (ToF) sensor is a device that measures the distance between the sensor and an object by calculating the time it takes for light to travel to the object and back. Typically, ToF sensors emit light (usually infrared or laser) towards a target and then measure how long it takes for the reflected light to return. Based on this time delay, the sensor calculates the distance to the object, allowing for the creation of a depth map or 3D representation of the surrounding environment. ToF sensors are commonly used in applications like 3D imaging, augmented reality (AR), robotics, and facial recognition
What Are Time-of-Flight Sensors?
Time-of-Flight sensors are specialized cameras or sensors that measure the distance between the sensor and objects by calculating the time it takes for emitted light (usually infrared or laser) to bounce off the object and return to the sensor. This principle is similar to how radar works, but instead of using sound waves, ToF sensors use light. The returned light data is then used to create a depth map, allowing for accurate three-dimensional (3D) modeling of the environment.
How Do ToF Sensors Work?
The working principle of a Time-of-Flight sensor is straightforward:
- Light Emission: The sensor emits a light signal, typically infrared or a laser pulse, in the direction of the target.
- Light Reflection: The light signal travels toward the object and reflects off it.
- Time Measurement: The sensor measures the time it takes for the light to return.
- Distance Calculation: By calculating the time delay (flight time), the sensor determines the distance to the object, forming a depth map.
Because ToF sensors emit and measure light at very high speeds, they can create real-time depth data with high accuracy and precision, even in challenging environments.
Benefits of Time-of-Flight Sensors
ToF sensors have numerous advantages, making them a preferred technology for 3D imaging and augmented reality applications. These benefits include:
- High Accuracy and Precision: ToF sensors provide precise depth measurements, making them ideal for 3D modeling and AR applications that require real-time data.
- Fast Data Processing: The speed at which ToF sensors capture and process data allows for instantaneous rendering of 3D environments, contributing to seamless augmented reality experiences.
- Low Power Consumption: ToF sensors are generally energy-efficient, making them suitable for mobile devices and other applications where battery life is a concern.
- Long Range: These sensors can measure distances over several meters, providing an extended field of view that is essential for many AR and 3D imaging scenarios.
- Robustness in Challenging Conditions: ToF sensors can perform well even in low-light conditions, making them versatile for various environments.
Applications of ToF Sensors in 3D Imaging
3D imaging involves capturing depth and spatial information about an object or environment and rendering that information in a three-dimensional form. Time-of-Flight sensors are fundamental in advancing this technology, as they offer precise, real-time data crucial for rendering 3D models. Below are some key applications of ToF sensors in 3D imaging:
1. Smartphones and Consumer Electronics
Many smartphones now come equipped with ToF sensors to enhance camera capabilities. These sensors enable features such as bokeh effects (background blur), object detection, facial recognition, and improved autofocus. By adding depth information to photographs and videos, ToF sensors allow users to take more dynamic and professional-quality images.
2. Industrial Robotics
In industrial environments, ToF sensors are used in robotic systems to enable precise object detection, distance measurement, and navigation. In manufacturing settings, for example, robots equipped with ToF sensors can assess the spatial layout of workspaces, identify obstacles, and optimize their movements in real time. This enhances efficiency, safety, and accuracy in automation processes.
3. Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous driving systems rely on several types of sensors, and ToF sensors are often used in combination with LiDAR and radar systems to detect obstacles and determine distances. These sensors help autonomous vehicles navigate complex environments, avoid collisions, and understand their surroundings in 3D.
4. Medical Imaging
ToF technology is also being applied in the medical field, where depth perception and accuracy are critical. For example, in surgical environments, ToF sensors can be used to guide robotic arms, assist in 3D imaging for diagnostic purposes, and ensure precise movements during procedures. These applications are particularly useful in minimally invasive surgeries where accurate 3D visualization is essential.
5. Security Systems
ToF sensors are often integrated into security and surveillance systems to create 3D representations of environments. These systems can detect intruders, monitor activities, and ensure perimeter security by capturing and analyzing depth information. Additionally, ToF technology enhances biometric security features such as facial recognition by providing more accurate depth data.
Role of ToF Sensors in Augmented Reality
Augmented reality (AR) involves overlaying digital content onto the physical world in real-time, allowing users to interact with both real and virtual environments. ToF sensors are critical to AR applications as they provide the depth data necessary to accurately map virtual objects onto physical spaces. Here are some of the ways ToF sensors contribute to augmented reality:
1. Improved Object Placement
One of the most important aspects of augmented reality is the accurate placement of virtual objects within the real world. ToF sensors provide detailed depth data that allows AR applications to place objects in precise locations relative to the user’s environment. This prevents virtual objects from floating awkwardly in the air and instead integrates them seamlessly with the physical world.
2. Enhanced Gesture Recognition
Interaction in augmented reality experiences depends on gesture recognition. ToF sensors enable more accurate detection of hand movements and gestures by capturing the depth and positioning of hands in 3D space. This improves the usability and responsiveness of AR applications, especially in gaming, virtual collaboration, and design tools.
3. Real-Time Environmental Mapping
ToF sensors allow AR devices to map an environment in real time, enabling users to move around and explore augmented spaces without losing track of virtual objects. This is crucial in applications like AR gaming, navigation, and architectural visualization, where users need to interact with both virtual and real elements continuously.
4. Virtual Try-Ons and Shopping
Retailers are increasingly adopting AR to enhance the shopping experience. ToF sensors make it possible for users to virtually try on products like clothes, glasses, or makeup by accurately capturing their dimensions and movements. This application improves customer engagement and helps users visualize how products will look in the real world.
Future of Time-of-Flight Sensors in 3D Imaging and AR
As ToF technology continues to improve, we can expect more innovative applications in 3D imaging and augmented reality. Potential future advancements include:
- Higher Resolution Depth Mapping: Improvements in sensor technology will lead to even higher resolution depth maps, enabling more detailed 3D models.
- Smaller and More Efficient Sensors: ToF sensors are becoming smaller and more power-efficient, which will make them even more suitable for mobile devices and wearables.
- Broader AR Integration: ToF sensors will likely become more integral to various AR applications, from education and training to gaming and social media.
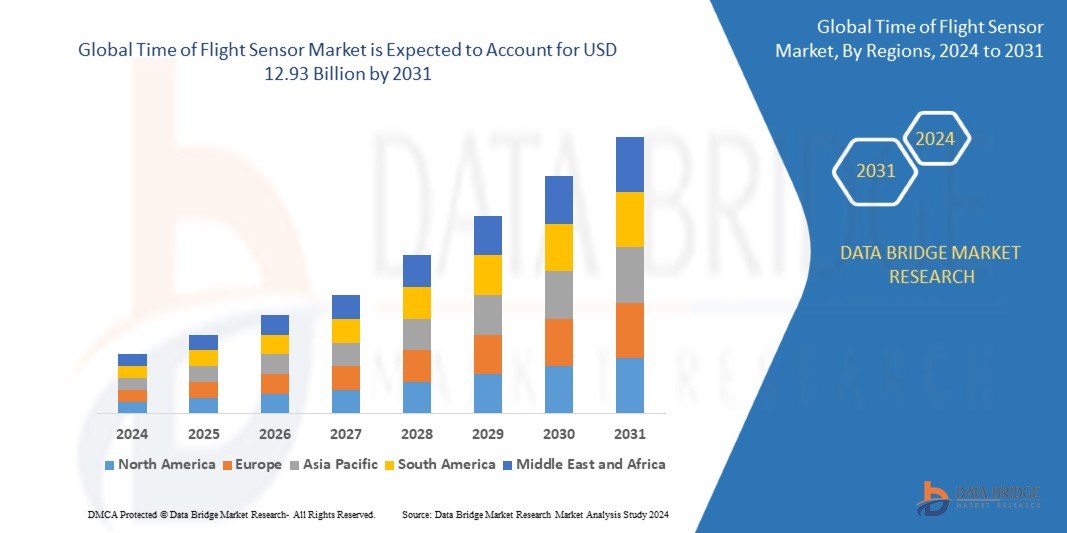
Growth Rate of Time of Flight Sensor Market
The size of the global Time of Flight Sensor Market was estimated at USD 3.70 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 16.95% from 2024 to 2031, reaching USD 12.93 billion.
Learn More: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-time-of-flight-sensor-market
Conclusion
Time-of-Flight sensors have transformed the fields of 3D imaging and augmented reality by offering precise, real-time depth information. Their applications across industries such as consumer electronics, robotics, medical imaging, and autonomous vehicles demonstrate the versatility and power of this technology. As the demand for 3D imaging and AR grows, ToF sensors will continue to play a pivotal role in advancing these technologies, shaping how we interact with both the digital and physical worlds.